Parking Space Occupancy
We like to see parking as two different sub use cases depending on where you place the parking sensor in relation to the car. ground placed and roof placed (indoor)/pole or wall mounted. We will go through the two variants separately and also take a look at a potential way of handling torrential rains with our Obstruction Detection functionality.
GROUND PLACED
The difficulties here is almost exclusively related to your product design and the climate the product is used in. Water/rain is non transparent substance, and it is not possible to configure a radar to see through water. You need to design your product so that water runs off the device as much as possible and ensure that water does not form a surface on top of your device.
Snow and ice are transparent. Unfortunately, snow/ice will at some point become water and might then cause problems. Besides the weather-related issues, it is very straight forward use case and we believe that our reference code is very close to product ready.

Obstruction Detection
In our Parking Reference Application, we have added a functionality we call Obstruction Detection. Simply the ability to see if the sensor is covered/blocked. This will come in handy in areas with heavy rain. If you want a completely weatherproof parking detector you could then utilize sensor fusion and simply switch to a magnetometer if your device is covered by rainwater.
It could also be very useful information for a parking company to get notified if a sensor is covered by some other reason. If someone tampered with the sensor or if it has accidentally become covered, they would be notified and can remove whatever blocks the sensor.

ROOF AND POLE
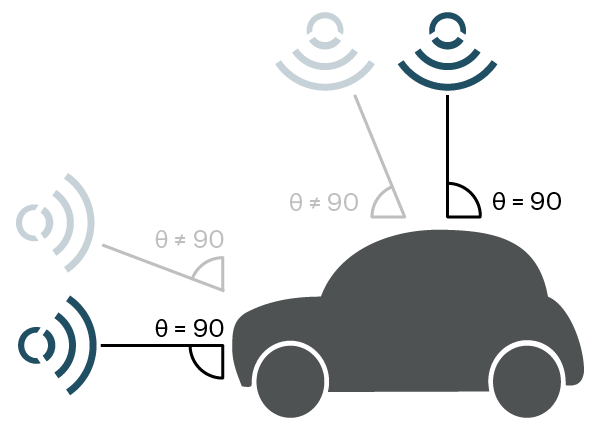
Roof and Pole mounted sensors are a little bit trickier. You might get rid of potential water problems but instead the angle of which the sensor points to the parking lot will become sensitive. One would think that a 1500 kilo piece of metal would be easy to detect but the sensor is not a camera. It is easy to place a sensor at an angle where zero reflections come back to the sensor. The closer a 90-degree angle you can be towards a flat surface of a car the better.
Pole mounted sensors are also sensitive in regard to the height the sensor is paced on the pole/wall. Optimal would be about the same height as the radiator grill/bumper of a standard car but often they have to be placed higher for practical reasons. Then there is a risk that the main part of the radiated wave hits the hood of the car and reflects away from the radar.
In summary. It is important to validate either the casings’ ability to lead off water, in case of ground place, or the optimal angle of the sensor in case it is placed in the roof or on a pole.
For more information and details about our reference application and it’s algorithms please go to: Parking — Acconeer docs
REFERENCE VIDEO PARKING
This video will give you an overview of our reference application capabilities.
